Original Source: NSO
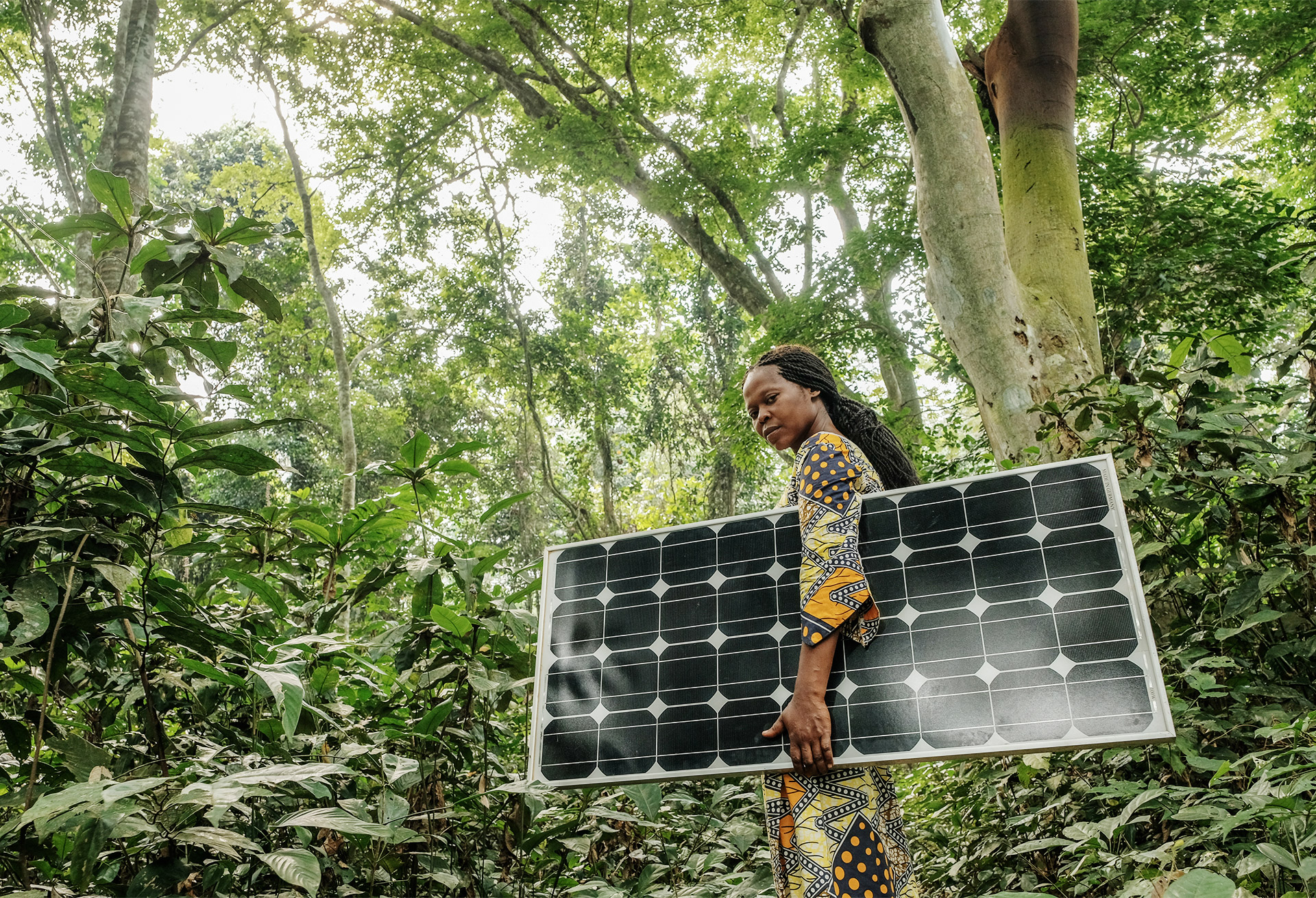
Smallholder farmers in Uganda are increasingly vulnerable to risks associated with changing weather patterns. The SUM-Africa project, supported by the G4AW program of Netherlands Space Office (NSO), provides satellite based drought index insurance to protect these smallholders. This week the Ugandan Agro Insurance Consortium (AIC) and the Dutch company EARS) signed a long-term contract to continue the delivery of this service. The AIC provides the insurance and EARS, lead partner in the Sum-Africa project, provides the satellite-based drought index.
Agricultural index insurance products are linked to an index, such as temperature, rainfall, crop yield or evapotranspiration, rather than actual loss. Daily information from satellites, enables independent and continuous monitoring of climatic conditions for crop growth. This information is used by insurance companies for risk assessment, insurance pricing, and for pay-out calculation. Because insurance companies no longer need to visit the farmer to assess their loss and determine payout, transaction costs are much lower. Insured farmers are more likely to get a loan, enabling them to invest in improved input that boost their resilience to climate change and increase their food production and income.
The Sum-Africa consortium consisting of eight African and Dutch partners, now rolls into its fifth year and starts operating on a commercial basis. An increasing number of farmers are being insured, with some 75,000 farmers insured in 2018. Sales numbers are expected to double over the next 2 years.
Click here to read full article